
There are two approaches to subnetting an IP address for a network: Fixed length subnet mask (FLSM) and variable-length subnet mask (VLSM). Figure 1.0 Diagram depicting supernetting Vs. With Supernetting, it will summarize them before sharing, which significantly reduces the size of routing updates. Without Supernetting, the router will share all routes from routing tables as they are. Routers share routing tables to find the new path and locate the best path for the destination. A routing table is a summary of all known networks. The main objective of supernetting is to simplify or summarize network routing decisions to minimize processing overhead when matching routes, and storage space of route information on routing tables. Supernetting provides route updates in the most efficient way possible by advertising many routes in one advertisement instead of individually. Supernetting is the direct opposite of subnetting, in which multiple networks are combined into a single large network known as supernets.

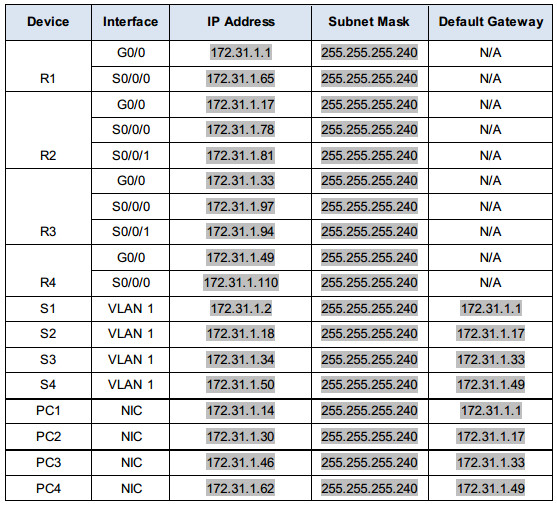
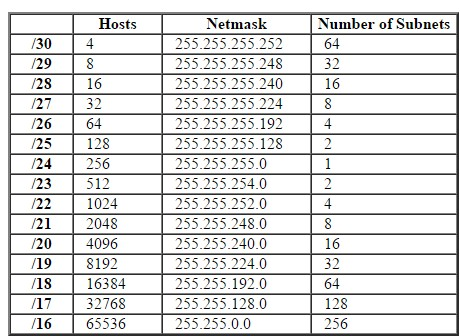
The primary purpose of subnetting is to help relieve network congestion and improve efficiency in the utilization of the relatively small network address space available especially in IPv4. Table 1.0 IP address and subnet mask in binary and decimal format SubnettingĪs the name implies, subnetting is the process of dividing a single large network into multiple small networks known as subnets. In shorthand, we use /24, which simply means that a subnet mask has 24 ones, and the rest are zeros. The ones designate the network prefix, while the trailing block of zeros designates the host identifier. An IPv4 subnet mask is a 32-bit sequence of ones (1) followed by a block of zeros (0). Subnet masks are used by a computer to determine if any computer is on the same network or on a different network.

In order to fully grasp the concept of VLSM, we first need to understand the term subnet mask, subnetting, and Supernetting.
#Subnet mask table 4 bits how to#
In this guide, we’re going to help you understand the concept of VLSM, and show you how to implement VLSM Subnetting. This eventually gave birth to what we now know as Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR), and Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM), which allows greater flexibility in the creation of sub-networks, overcoming the strict rules of the A, B, and C classes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
